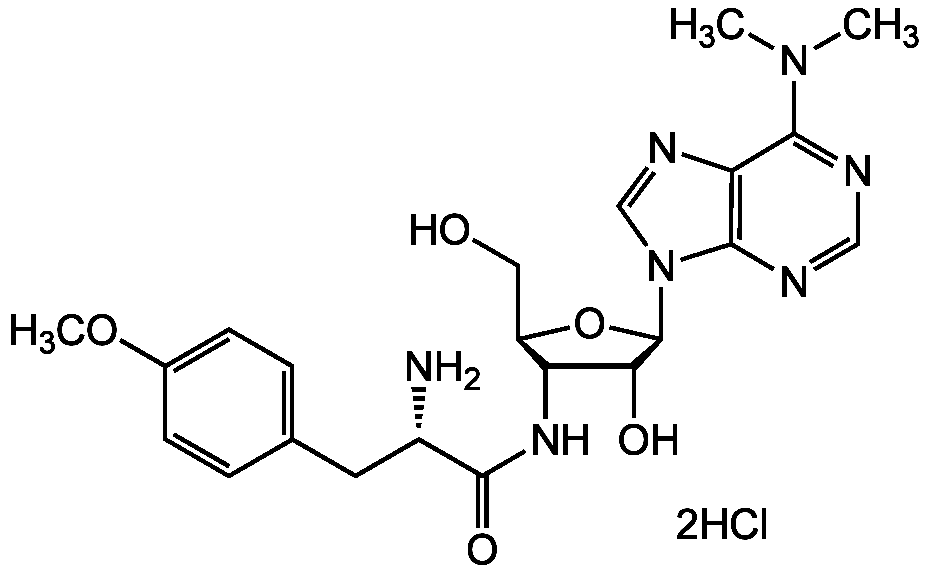
Puromycin . dihydrochloride
Aminonucleoside antibiotic. Protein synthesis inhibitor. Disrupts peptide transfer on ribosomes (acting as an acyl-tRNA analog) causing premature chain termination during translation. Translational inhibitor in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in both in vitro and in vivo systems. Inhibits the transport of proteins into the mitochondria in vitro. Reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase II (serine peptidase) and cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase (metallopeptidase). Apoptosis inducer. Inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria, various animal and insect cells. Fungi and Gram-negative bacteria are resistant due to the low permeability to the antibiotic. Antineoplastic agent. Used in cell biology as selective agent in cell culture systems. It allows selection for cells that contain the resistance gene puromycin N-acetyl-transferase (PAC). Puromycin has a fast mode of action, causing rapid cell death at low antibiotic concentrations. Adherent mammalian cells are sensitive to concentrations of 2 to 5 µg/ml, while cells in suspension are sensitive to concentrations as low as 0.5 to 2 µg/ml. Puromycin-resistant stable mammalian cell lines can be generated in less than one week.
| Catalog Number | AG-CN2-0078-M100 |
| Alternative Name(s) | CL16,536; NSC 3055; Stylomycin |
| Research Area | Antibiotic, Apoptosis, Cancer, Cell Death, Natural Products |
| Molecular Formula | C22H29N7O5 . 2HCl |
| CAS# | 58-58-2 |
| Purity | >98% |
| Inchi | InChI=1/C22H29N7O5/c1-28(2)19-17-20(25-10-24-19)29(11-26-17)22-18(31)16(15(9-30)34-22)27-21(32)14(23)8-12-4-6-13(33-3)7-5-12/h4-7,10-11,14-16,18,22,30-31H,8-9,23H2,1-3H3,(H,27,32)/t14-,15+,16?,18?,22+/m0/s1 |
| Inchi Key | RXWNCPJZOCPEPQ-NIAQAADTBJ |
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C[C@H](N)C(=O)NC2[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]([C@H]2O)N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N(C)C)C=C1 |
| Size | 100 mg |
| Supplier Page | http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0078/puromycin-dihydrochlorid.html |

