TargetMol
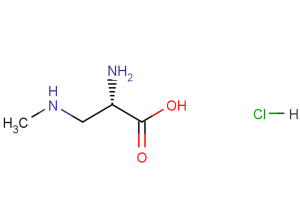
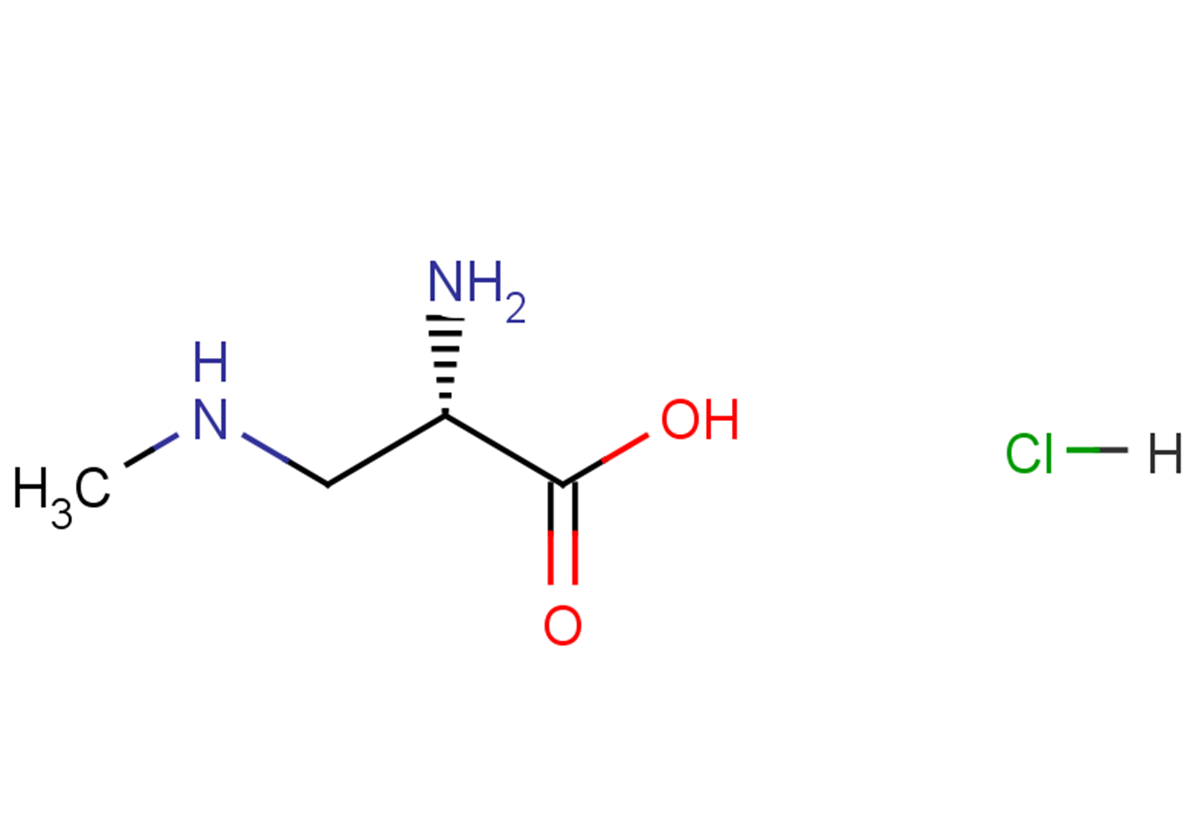
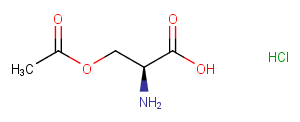
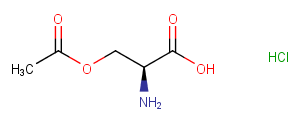
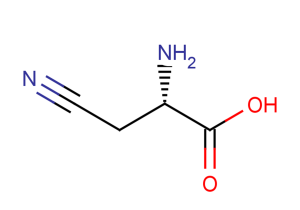
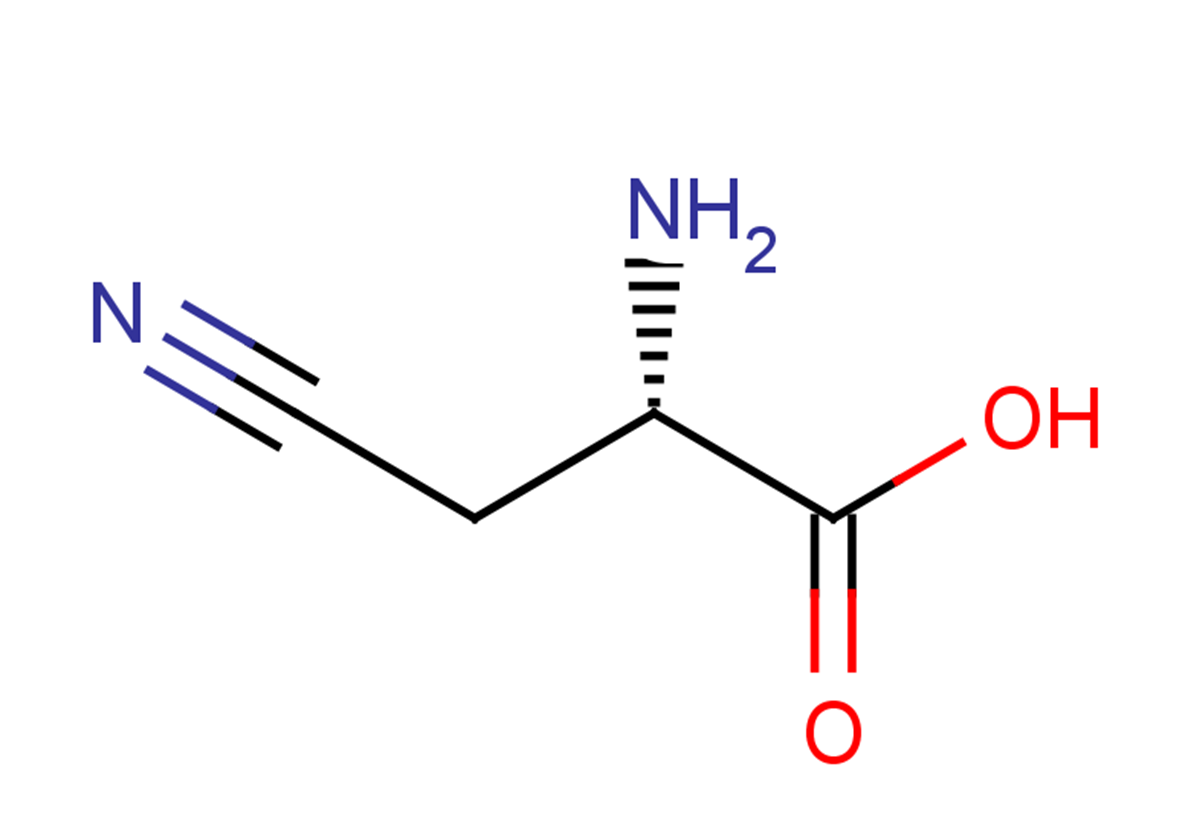
β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride (L-BMAA hydrochloride) is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria. L-BMAA hydrochloride could cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and possibly other neurodegenerative diseases.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Naphthoflavone-CH2-Br is an arylhydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligand. β-Naphthoflavone-CH2-Br used to synthesize the PROTAC β-NF-JQ1.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
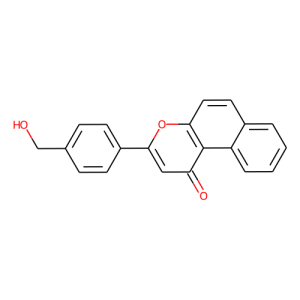
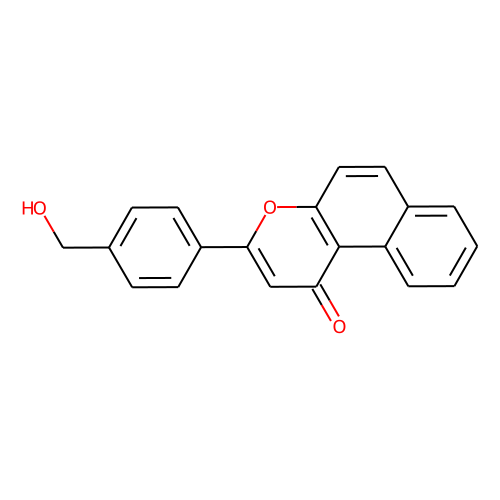
β-Naphthoflavone-CH2-OH (β-NF-CH2-OH) serves as an AhR E3 ligase ligand, forming chimeric molecules when connected to a protein ligand through a linker, resulting in PROTACs or SNIPERs (e.g., β-naphthoflavone-JQ1). These chimeric molecules recruit the AhR E3 ligase complex by incorporating AhR ligands. By inducing ubiquitination-mediated degradation, PROTACs effectively target and degrade cancer-promoting proteins [1].
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Naphthoflavone-CH2-OH (β-NF-CH2-OH) serves as an AhR E3 ligase ligand, forming chimeric molecules when connected to a protein ligand through a linker, resulting in PROTACs or SNIPERs (e.g., β-naphthoflavone-JQ1). These chimeric molecules recruit the AhR E3 ligase complex by incorporating AhR ligands. By inducing ubiquitination-mediated degradation, PROTACs effectively target and degrade cancer-promoting proteins [1].
More Information
Supplier Page
β-NETA
1 mL
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
α-NETA is a stable, noncompetitive, slowly reversible choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) inhibitor with an IC50 of 9 μM and is a potent chemokine-like receptor-1 (CMKLR1) antagonist. α-NETA has anti-cancer activity[1][2]. α-NETA weakly inhibits cholinesterase (IC50=84 µM) and acetylcholinesterase (IC50=300 µM).
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
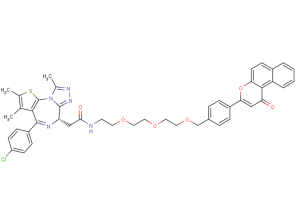
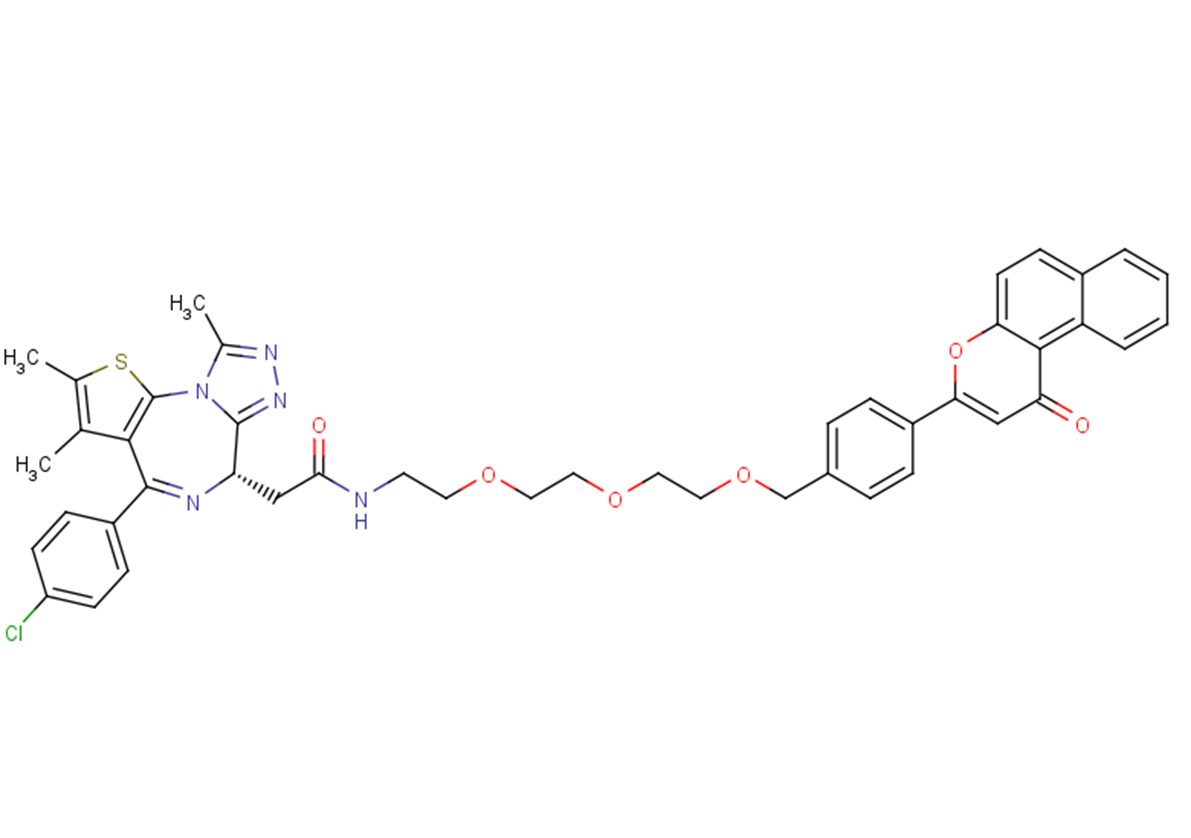
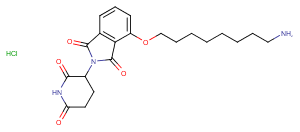
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-NF-JQ1 is a PROTAC that recruits aryl hydrocarbon receptor E3 (AhR E3) ligase to target proteins. β-NF-JQ1 uses β-NF as an AhR ligand to target bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and induce AhR and BRD protein interactions. β-NF-JQ1 shows potent anticancer activity associated with protein knockdown activity. .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
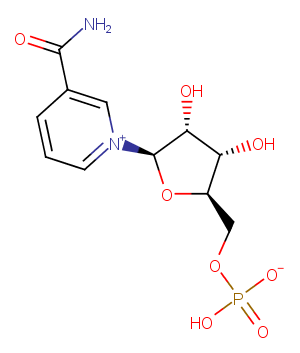
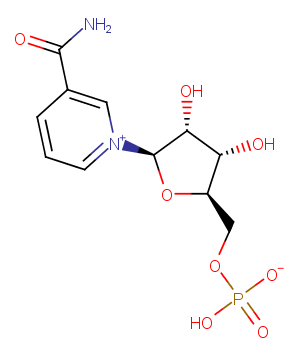
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium is an orally active reduced coenzyme. β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium is a donor of ADP-ribose units in ADP-ribosylaton reactions and a precursor of cyclic ADP-ribose. β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium plays a role as a regenerative electron donor in cellular energy metabolism, including glycolysis, β-oxidation and the tricarboxylic acid […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium is an orally active reduced coenzyme. β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium is a donor of ADP-ribose units in ADP-ribosylaton reactions and a precursor of cyclic ADP-ribose. β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium plays a role as a regenerative electron donor in cellular energy metabolism, including glycolysis, β-oxidation and the tricarboxylic acid […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NM) is an important intermediate metabolite in the nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathway. Mammals predominantly use nicotinamide rather than nicotinic acid as a precursor for NAD biosynthesis. Instead of the deamidation to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide is directly converted to β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT, EC 2.4.2.12). The enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT, […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
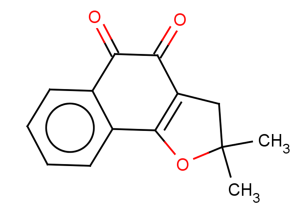
β-Nor-lapachone is an antibiofilm agent of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone can stimulate ROS production, inhibits efflux activity, adhesion, biofilm formation and the metabolism of mature biofilms of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone has antifungal activity [1].
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nor-lapachone is an antibiofilm agent of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone can stimulate ROS production, inhibits efflux activity, adhesion, biofilm formation and the metabolism of mature biofilms of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone has antifungal activity [1].
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Nor-lapachone is an antibiofilm agent of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone can stimulate ROS production, inhibits efflux activity, adhesion, biofilm formation and the metabolism of mature biofilms of Candida glabrata. β-Nor-lapachone has antifungal activity [1].
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Phellandrene (p-mentha-1(7),2-diene) is found in allspice. beta-Phellandrene is widely distributed in essential oils
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
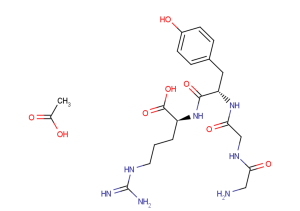
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate is a wasp venom peptide. β-Pompilidotoxin Acetate can slow sodium channel inactivation and increase steady-state sodium current in cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin TFA (β-PMTX TFA), a wasp venom, can slow sodium channel inactivation and increases steady-state sodium current in cells [1] .
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Pompilidotoxin TFA (β-PMTX TFA), a wasp venom, can slow sodium channel inactivation and increases steady-state sodium current in cells [1] .
More Information
Supplier Page
β-Rubromycin
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
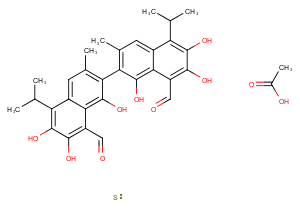
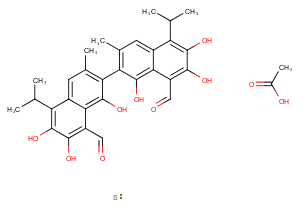
β-Rubromycin is a bacterial metabolite originally isolated from Streptomyces that has diverse biological activities.1 It inhibits the growth of HMO2, KATO-III, and MCF-7 cells with GI50 values of 0.5, 0.84, and
More Information
Supplier Page
β-Rubromycin
5 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
β-Rubromycin is a bacterial metabolite originally isolated from Streptomyces that has diverse biological activities.1 It inhibits the growth of HMO2, KATO-III, and MCF-7 cells with GI50 values of 0.5, 0.84, and
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
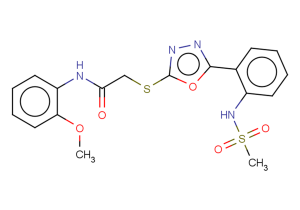
β-Secretase Inhibitor I is a highly potent inhibitor of the β-secretase enzyme. This compound exhibits exceptional inhibitory activity while also demonstrating a significant reduction in cardiovascular and liver toxicity.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
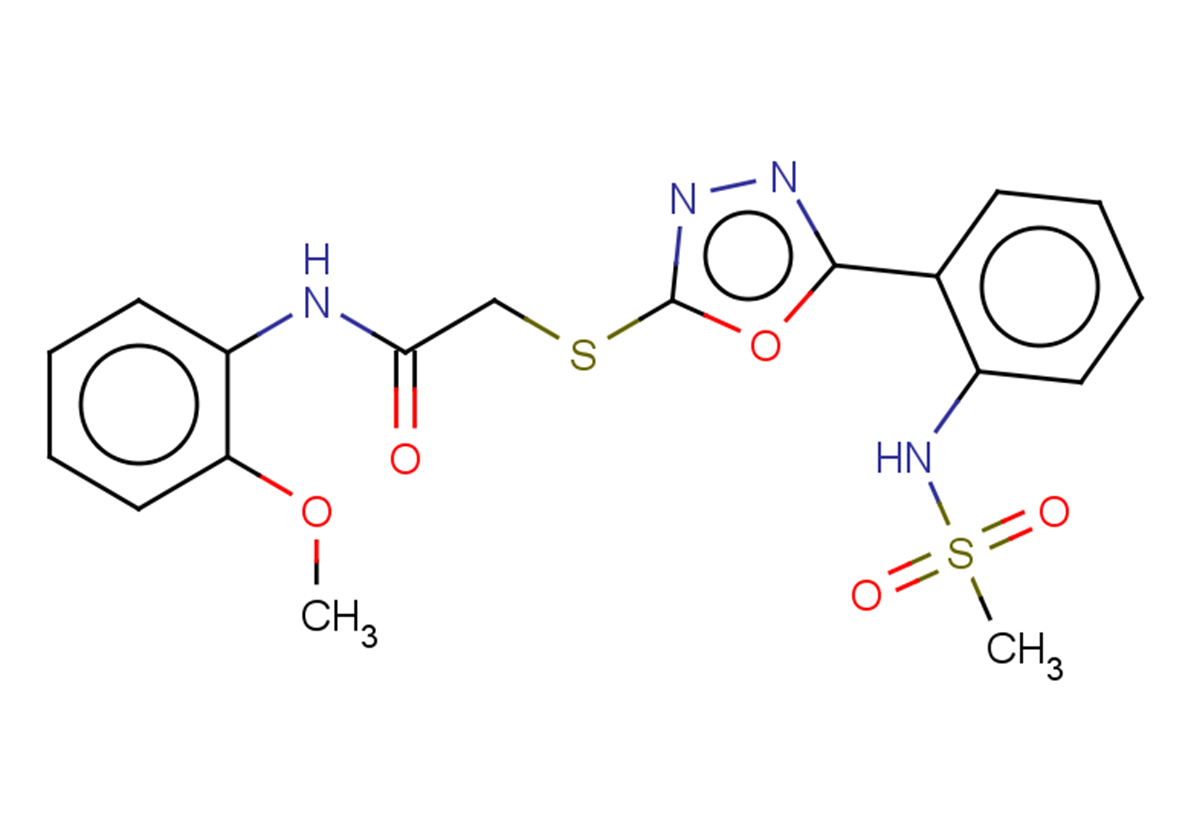
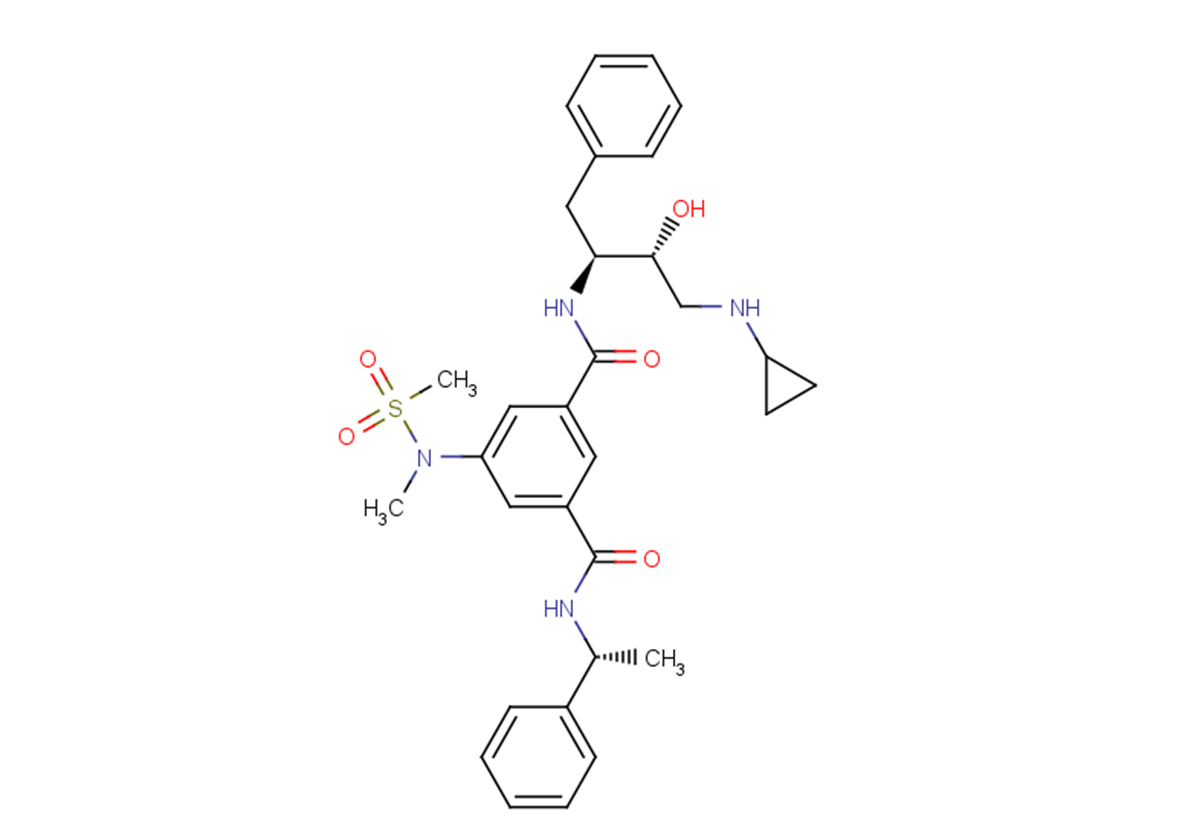
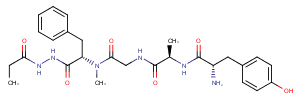
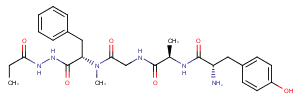
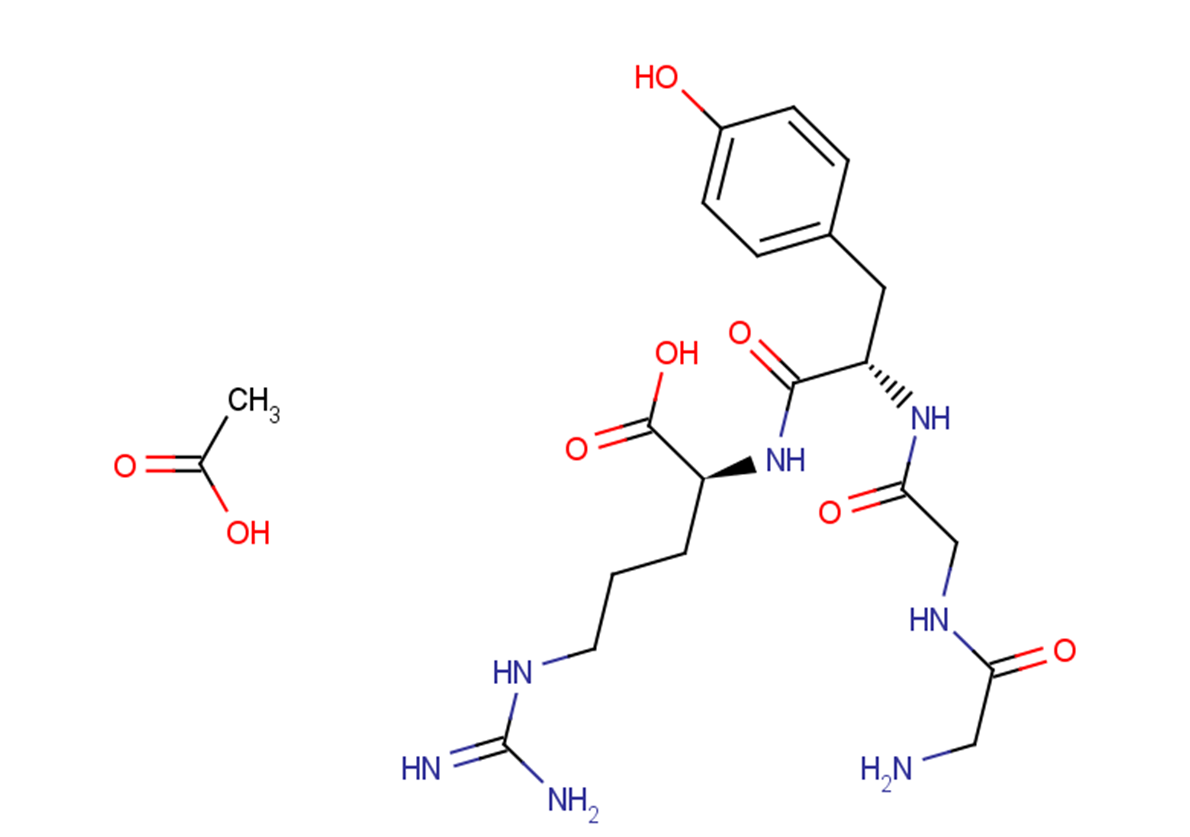
β-Secretase Inhibitor II is a tripeptide aldehyde compound that acts as an inhibitor of β-Secretase. It exhibits a simple structure and has an inhibitory potency of IC50 = 700 nM against total Aβ and IC50 = 2.5 μM specifically against Aβ 1-42. This compound is particularly useful in research related to Alzheimer’s disease.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
TargetMol
TargetMol
TargetMol
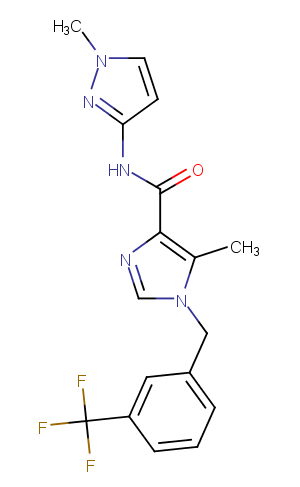
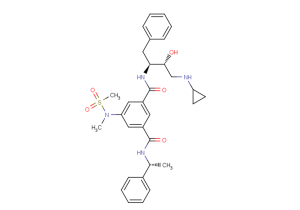
β-Secretase Inhibitor IV is a potent, cell-active inhibitor of BACE-1(IC50s of 15.6 and 16.3nM under BACE-1 concentrations of 2 nM and 100 pM, respectively).
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Secretase Inhibitor IV is a potent, cell-active inhibitor of BACE-1(IC50s of 15.6 and 16.3nM under BACE-1 concentrations of 2 nM and 100 pM, respectively).
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Secretase Inhibitor IV is a potent, cell-active inhibitor of BACE-1(IC50s of 15.6 and 16.3nM under BACE-1 concentrations of 2 nM and 100 pM, respectively).
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
β-Tocotrienol
50 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
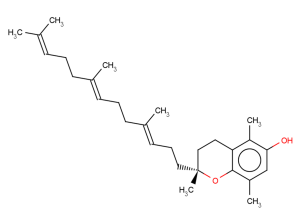
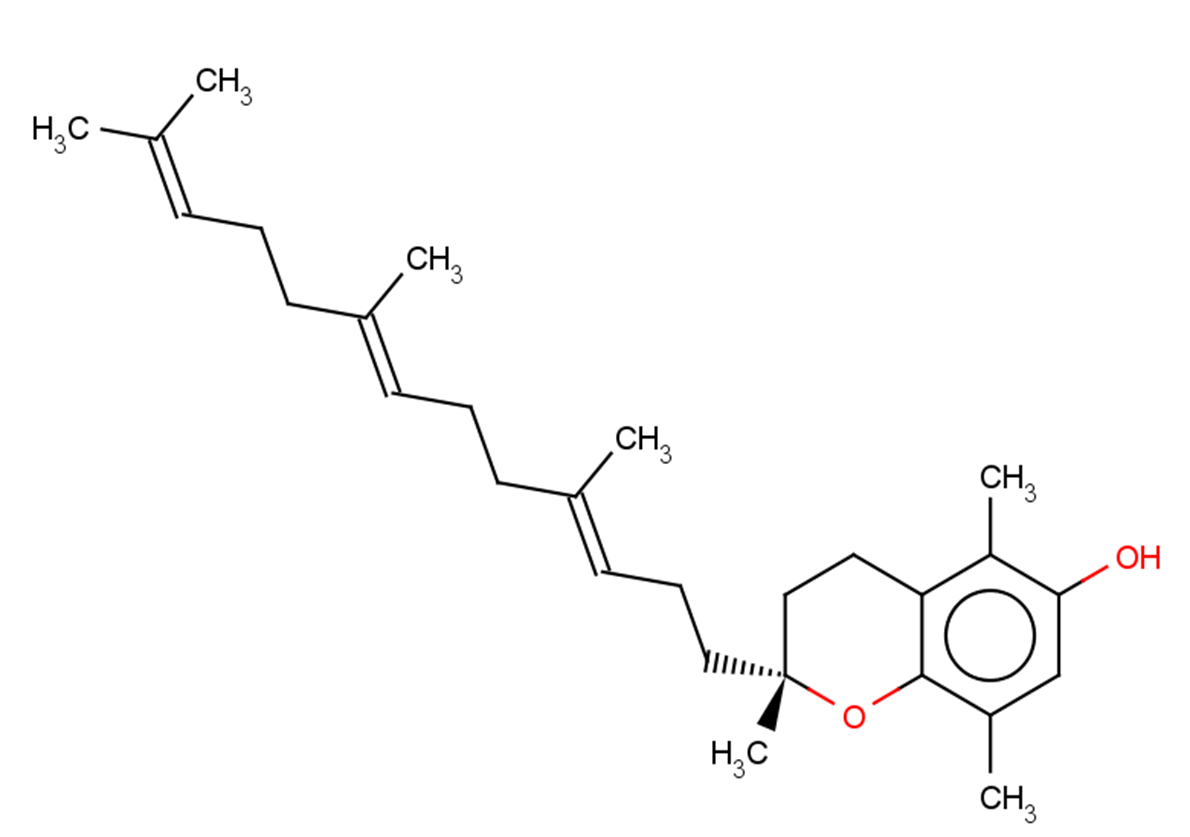
Beta-Tocotrienol to serve as a new anticancer agent for treating human lung and brain cancers. It inhibits the growth of both A549 (GI50=1.38±0.334μM) and U87MG (GI50=2.53±0.604μM) cells at rather low concentrations.
More Information
Supplier Page
β-Tocotrienol
100 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Beta-Tocotrienol to serve as a new anticancer agent for treating human lung and brain cancers. It inhibits the growth of both A549 (GI50=1.38±0.334μM) and U87MG (GI50=2.53±0.604μM) cells at rather low concentrations.
More Information
Supplier Page
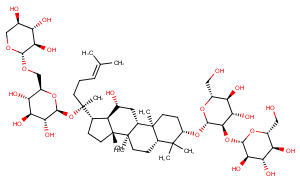
β-Tomatine
25 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
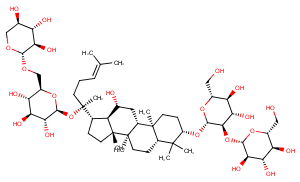
β-Tomatine, a derivative of α-tomatine, is a fungitoxic compound that efficiently inhibits plant defense responses.
More Information
Supplier Page
β-Zearalenol
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
β-Zearalenol, a non-steroidal estrogenic mycotoxin synthesized by Fusarium species, potentially influences transcription and affects gene expression on the translational level.
More Information
Supplier Page