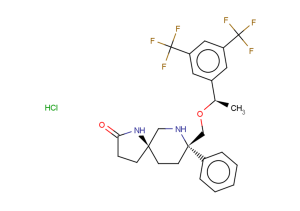
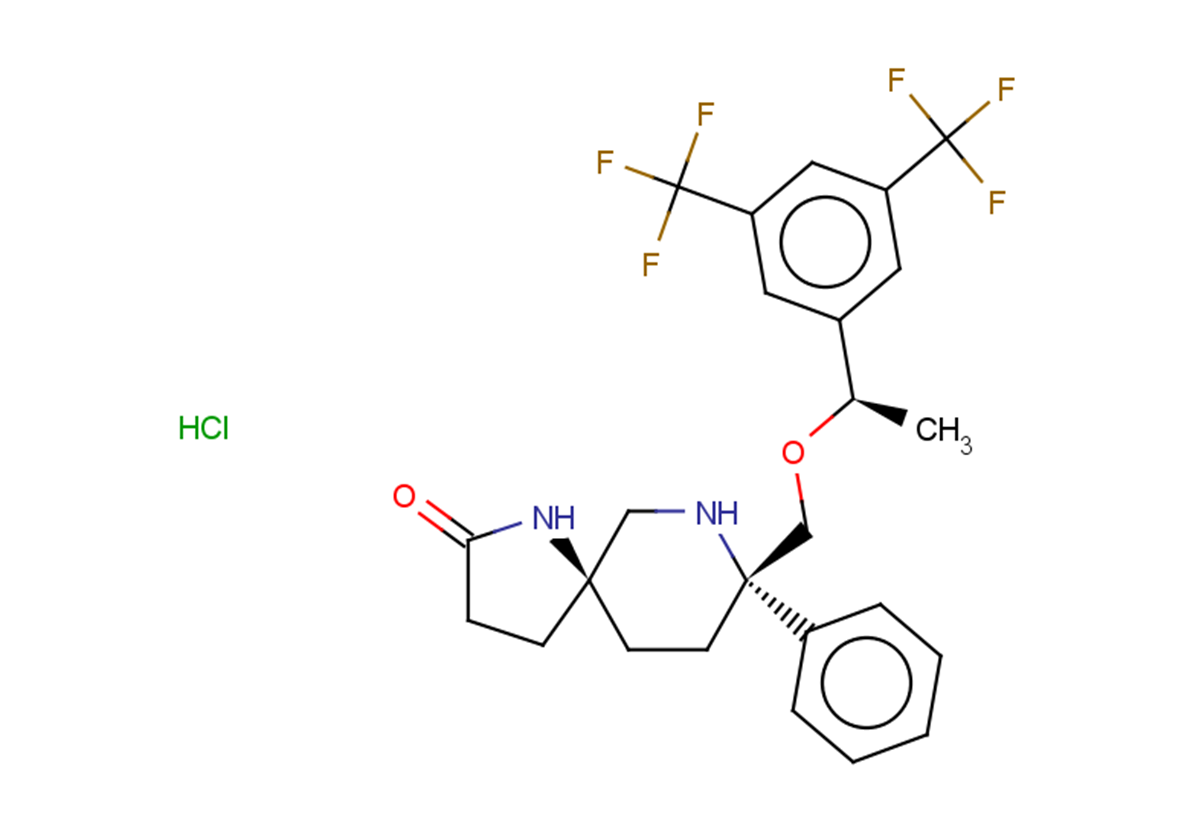
TargetMol
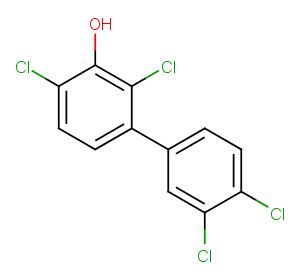
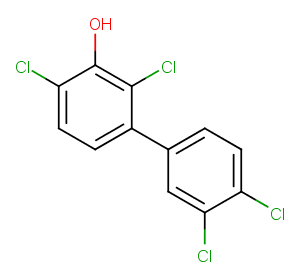
(±)19(20)-EpDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid . It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA and can be further metabolized to (±)19(20)-DiHDTE by epoxide hydrolase.
More Information
Supplier Page
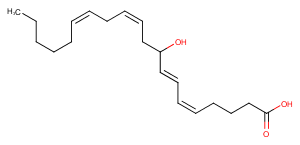
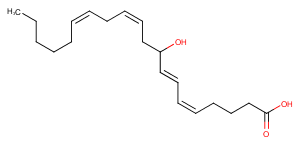
(±)20-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)4-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)4-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells also produces 4-HDHA. However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)4-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)5(6)-DiHET lactone is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHET , which, in turn, is a potential derivative of epoxidation of arachidonic acid at the α-5 double bond. (±)4(5)-DiHDPA lactone is a derivative of docosahexaenoic acid that is analogous to (±)5(6)-DiHET lactone. It is the 1,4 cyclic ester derived from (±)4(5)-DiHDPA, which is produced by […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester is a derivative of (±)4(5)-EpDPA which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely. The active free acid can be regenerated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. (±)4(5)EpDPA is a CYP450 metabolite of DHA which can be further metabolized to the diol metabolite. There are no published reports on the […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)5-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)5-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HEPE and 5(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)5-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 5(S) isomer in mammalian systems. EPA can be metabolized to 5-HEPE in human and bovine neutrophils, and human eosinophils, which is further […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)5-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HETE and 5(R)-HETE. (±)5-HETE induces the aggregation of isolated neutrophils with an IC50 value of 200 nM.[1]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)5-iPF2α-VI
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Isoprostanes are prostaglandin (PG)-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation. Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes. (±)5-iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
5,6-DiHET lactone is a lactonized form of 5,6-EET and 5,6-DiHET. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5(6)-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS. 5,6-DiHET potently induces vasodilation of isolated canine coronary arterioles, with 41 and 100% inhibition occurring at 0.01 and 100 pM, respectively. It also induces vasodilation in isolated […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
Eicosapentaenoic acid is an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundant in marine organisms and fish oils. EPA is metabolized, in part, through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation followed by conversion to the vicinal diols by epoxide hydrolases. (±)5(6)-DiHETE is a possible metabolite produced from EPA following epoxidation of the α-5 double bond. The biological activity of […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
Eicosapentaenoic acid is metabolized, in part, through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation followed by conversion to the vicinal diols by epoxide hydrolases. (±)5(6)-DiHETE is a possible metabolite produced from EPA following epoxidation of the α-5 double bond. (±)5(6)-DiHETE lactone is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHETE. While its biological activity is unknown, the selective capacity of […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)5(6)-EET
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
5(6)-EET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid by cytochrome P450 enzymes. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5,6-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS. In neuroendocrine cells, such as the anterior pituitary and pancreatic islets, 5(6)-EET has been implicated in the mobilization of […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)5(6)-EpETE methyl ester is a derivative of 5(6)-EpETE which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely.(±) 5(6)-EpETE methyl ester is a chemically less reactive derivative of 5(6)-EpETE. The active free acid can be generated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. Epoxy eicosatetraenoic acids (EpETEs) are the epoxygenase metabolites of EPA. A number […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)7-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)7-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells and human neutrophils also produces 7-HDHA. However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)7-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)7(8)-DiHDPA is a major metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid that is produced via oxidation by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases. Epoxygenase metabolites of DHA, including (±)7(8)-DiHDPA, suppress aggregation and thromboxane synthesis in isolated platelets.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)7(8)-EpDPA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Docosahexaenoic acid is the most abundant ω-3 fatty acid in neural tissues, especially in the brain and retina. (±)7(8)-EpDPA is an epoxide derivative of DHA that is generated by the action of cytochrome P450 epoxygenases. It is naturally occurring in plasma and brain and spinal cord tissues and is increased following dietary supplementation with ω-3 […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)7(8)-EpDTE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)7(8)-EpDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid . It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA, and can be further metabolized to (±)7(8)-DiHDTE by epoxide hydrolase.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)8-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)8-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. (±)8-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)8-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)8-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 8(S)-HEPE and 8(R)-HEPE. The ability of (±)8-HEPE to induce hatching of E. modestus and B. balanoides eggs is probably due to the presence of the 8(R) isomer within the racemic mixture.[1][2]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)8,9-DiHETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)8,9-DiHETE is a major metabolite of the 20:5 ω-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid .[1] It is produced in rat liver microsomes, but not renal microsomes, by the generation of the unstable intermediate 8,9-epoxy eicosatetraenoic acid from EPA by cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. Dietary EPA supplementation in humans results in substantial urinary excretion of vicinal diols, including […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)8(9)-DiHET
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Epoxide hydrolases convert the EETs into vicinal diols, with the concurrent loss of much of their biological activity. The 8(S),9(R)-EET isomer is metabolized by platelet COX to form 8(S),9(R),11(R)-THETA, a trihydroxy fatty acid which may act as a renal vasoconstrictor.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)14(15)-EE-8(Z)-E is a potent vasodilator in bovine coronary arteries. The synthesis of this analog involves the formation of the epoxide at the 14,15-double bond, however, epoxidation can also occur at the 8,9-double bond. (±)8(9)-EE-14(Z)-E is a minor product from the synthesis of (±)14(15)-EE-8(Z)-E. This compound has not been reported in the literature, and its biological […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)8(9)-EpETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Eicosapentaenoic acid is converted to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETEs) by several cytochrome P450 isoforms. The major product of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE , relaxes vascular and airway smooth muscle by activating large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels by directly interacting with BKα channel subunits. (±)8(9)-EpETE is an epoxygenase pathway product produced from EPA by CYP450 both […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)9-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)9-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 9(S)-HEPE and 9(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)9-HEPE has not been clearly documented.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)9-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)9-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The individual R and S isomers of racemic HETEs have been separated and identified using chiral phase HPLC. The racemic HETEs have been quantified as an index of lipid peroxidation using GC/MS.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)9-HODE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)9-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. Approximately equal proportions of both isomers are found in mitochondrial and plasma membranes of rabbit reticulocytes. [1][2] Oxidized LDL contains significant amounts of esterified 9- and 13-HpODEs and HODEs. [3][4]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)9-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL. Later studies determined that 15-LO from rabbit reticulocytes and human monocytes were able to metabolize cholesteryl linoleate, a major component of LDL, to 9-HODE cholesteryl ester.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)9-HpODE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)9-HpODE is a racemic mixture of the fatty acid hydroperoxide product (9(S)-HpODE) formed from lipoxygenase action on linoleic acid. It shows antimicrobial activity against various fungal and bacterial pathogens and thus may play a role in plant defense. In mammalian species, monocyte-induced oxidization of LDL generates significant amounts of esterified 9-HpODE, which is rapidly reduced […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
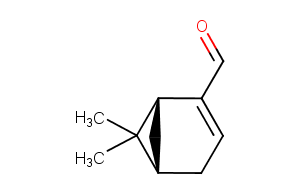
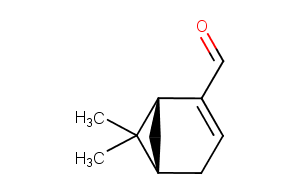
(−)-Myrtenal ameliorates hyperglycemia by enhancing GLUT2 through Akt in the skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(−)-Myrtenal ameliorates hyperglycemia by enhancing GLUT2 through Akt in the skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(−)-Myrtenal ameliorates hyperglycemia by enhancing GLUT2 through Akt in the skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
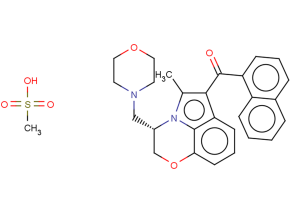
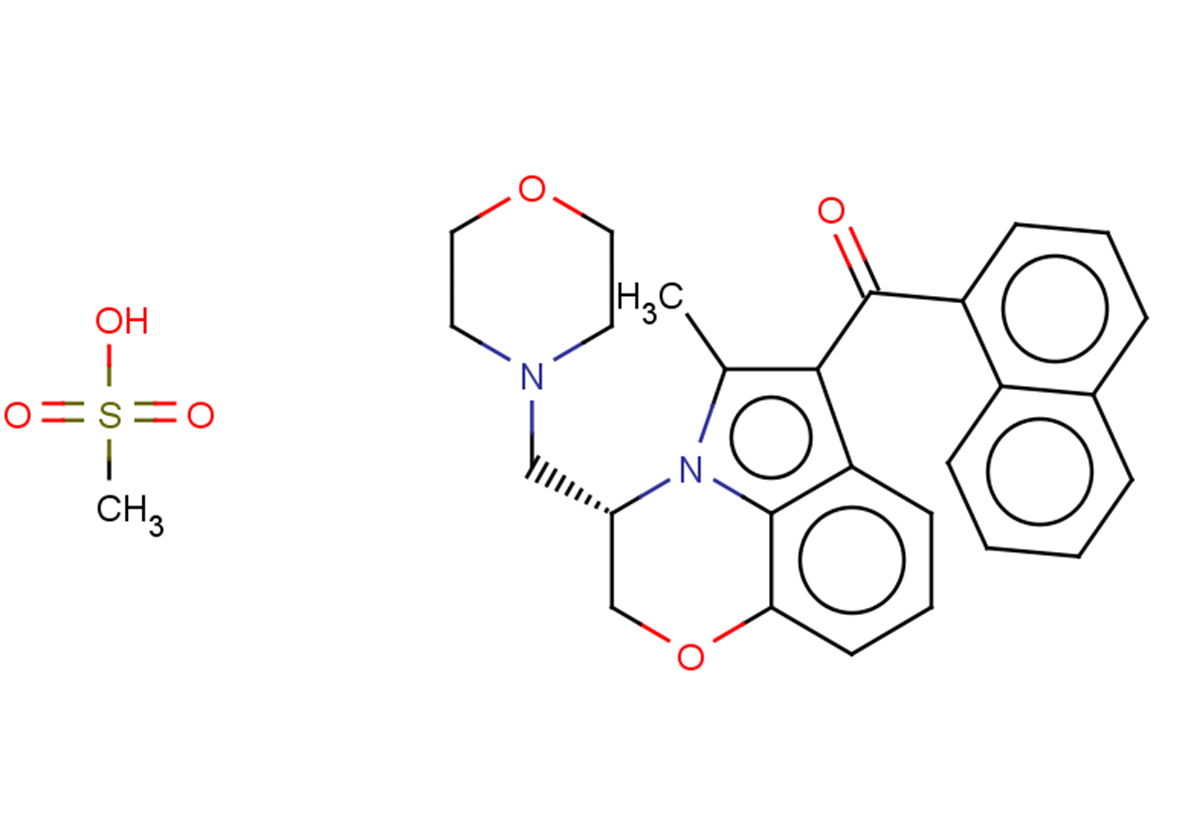
(−)-WIN 55,212-3 mesylate is an aminoalkylindole derivative which acts as a competitive neutral antagonist of the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor, blocking both the stimulating action of CP 55,940 and the inverse agonism of SR 144528. (−)-WIN 55,212-3 neither antagonizes nor mimics the effects of Δ9-THC on rat cerebellar membranes, which presumably express the CB1 receptor. […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(−)-WIN 55,212-3 mesylate is an aminoalkylindole derivative which acts as a competitive neutral antagonist of the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor, blocking both the stimulating action of CP 55,940 and the inverse agonism of SR 144528. (−)-WIN 55,212-3 neither antagonizes nor mimics the effects of Δ9-THC on rat cerebellar membranes, which presumably express the CB1 receptor. […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(−)-WIN 55,212-3 mesylate is an aminoalkylindole derivative which acts as a competitive neutral antagonist of the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor, blocking both the stimulating action of CP 55,940 and the inverse agonism of SR 144528. (−)-WIN 55,212-3 neither antagonizes nor mimics the effects of Δ9-THC on rat cerebellar membranes, which presumably express the CB1 receptor. […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
TargetMol
TargetMol
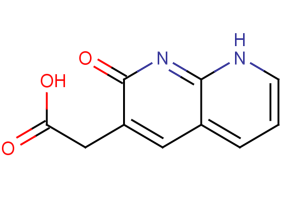
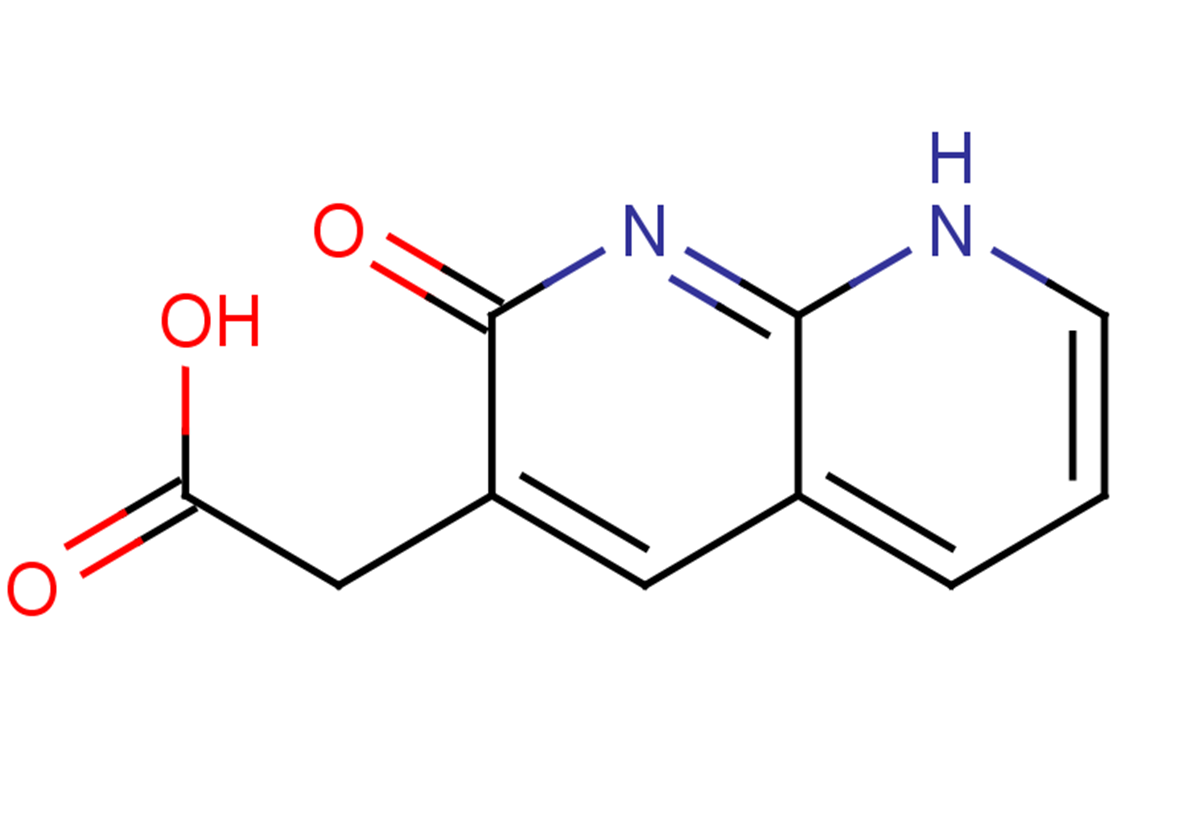
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; intermediate and building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
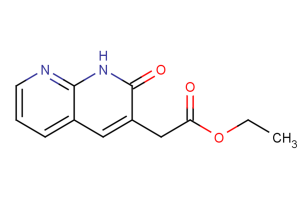
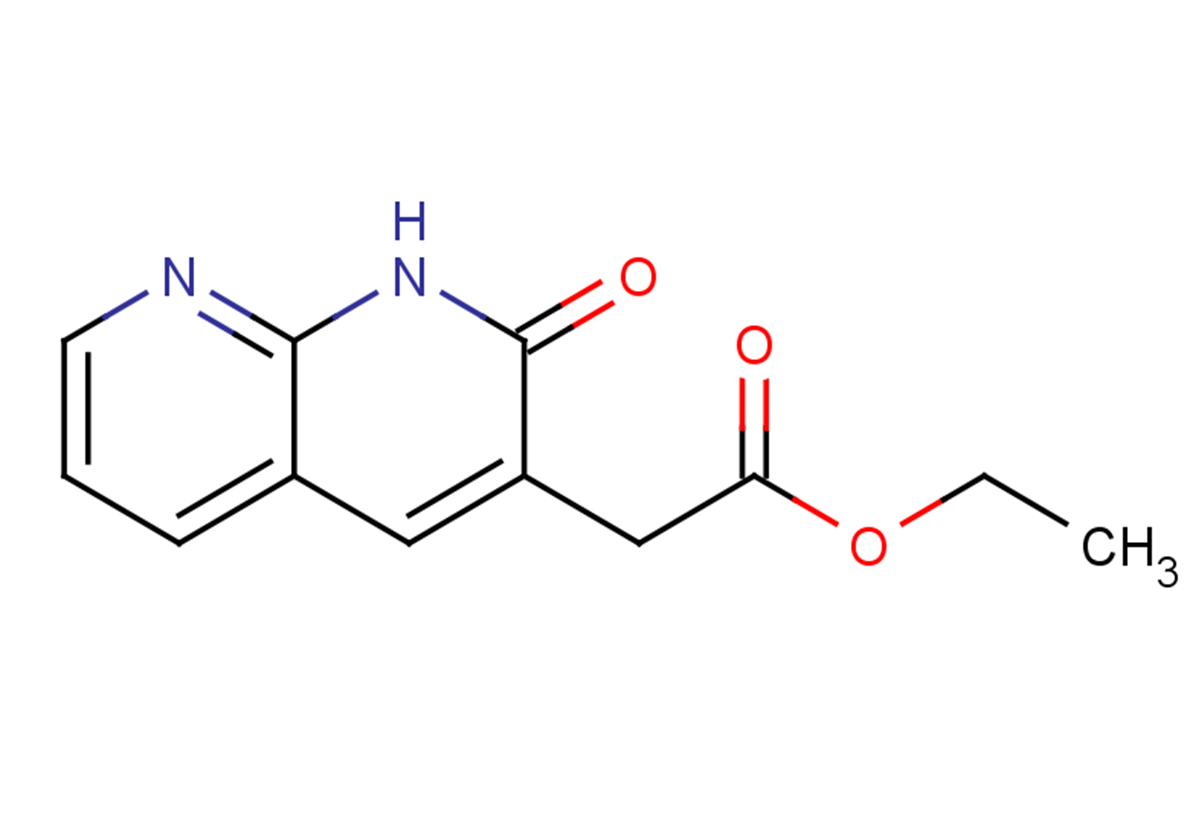
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester is a PNA-related derivative; heterocyclic compound-Fused polyheterocycle; building blocks.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
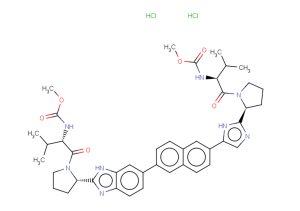
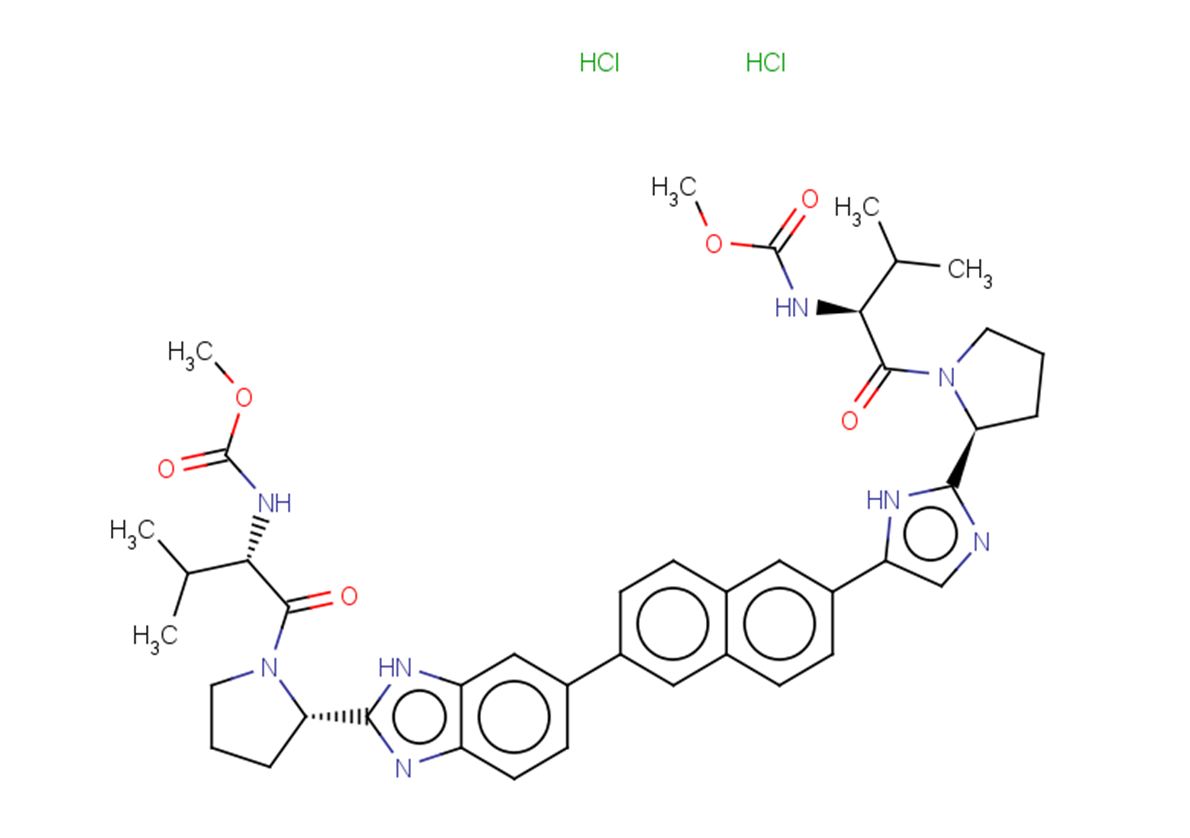
(1,5E,11E)-tridecatriene-7,9-diyne-3,4-diacetate is a natural product for research related to life sciences. The catalog number is TN2506 and the CAS number is 201012-14-8.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(1,5E,11E)-tridecatriene-7,9-diyne-3,4-diacetate is a natural product for research related to life sciences. The catalog number is TN2506 and the CAS number is 201012-14-8.
More Information
Supplier Page