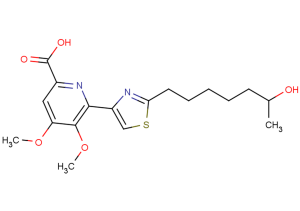
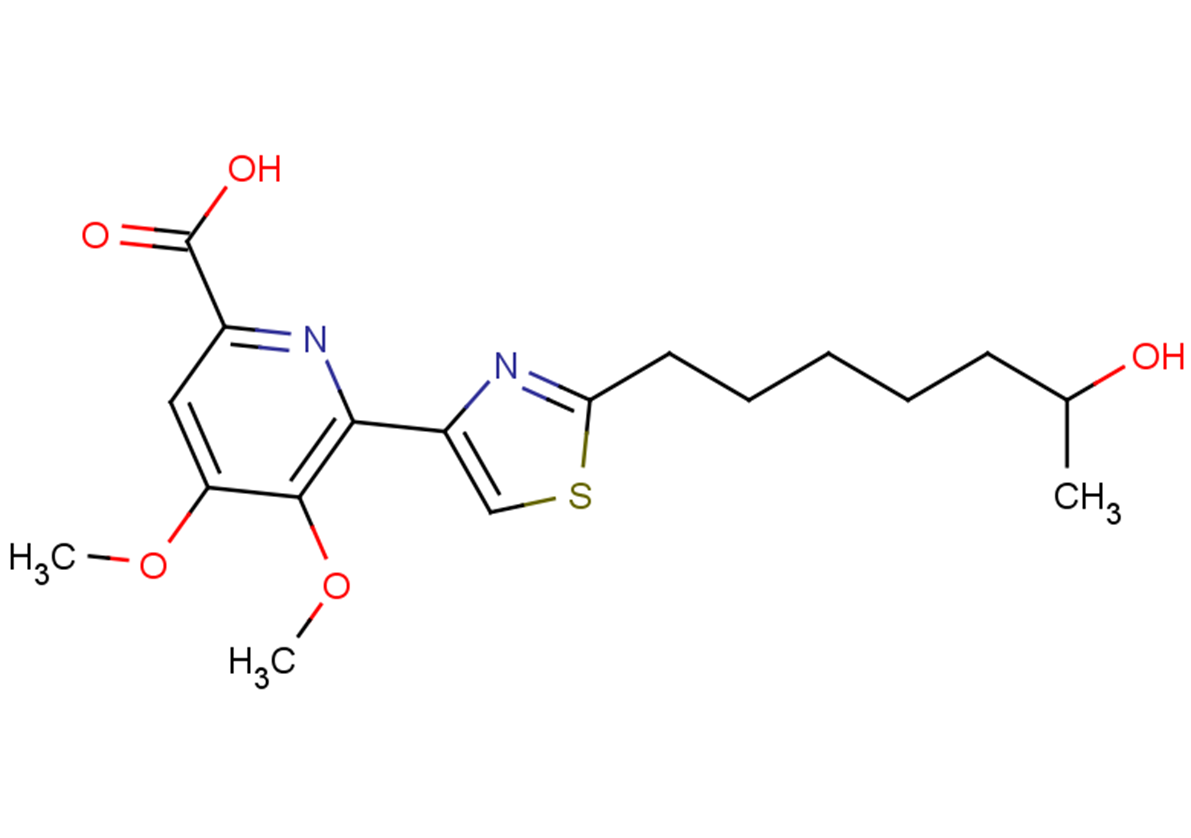
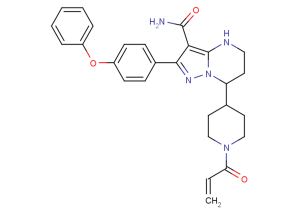
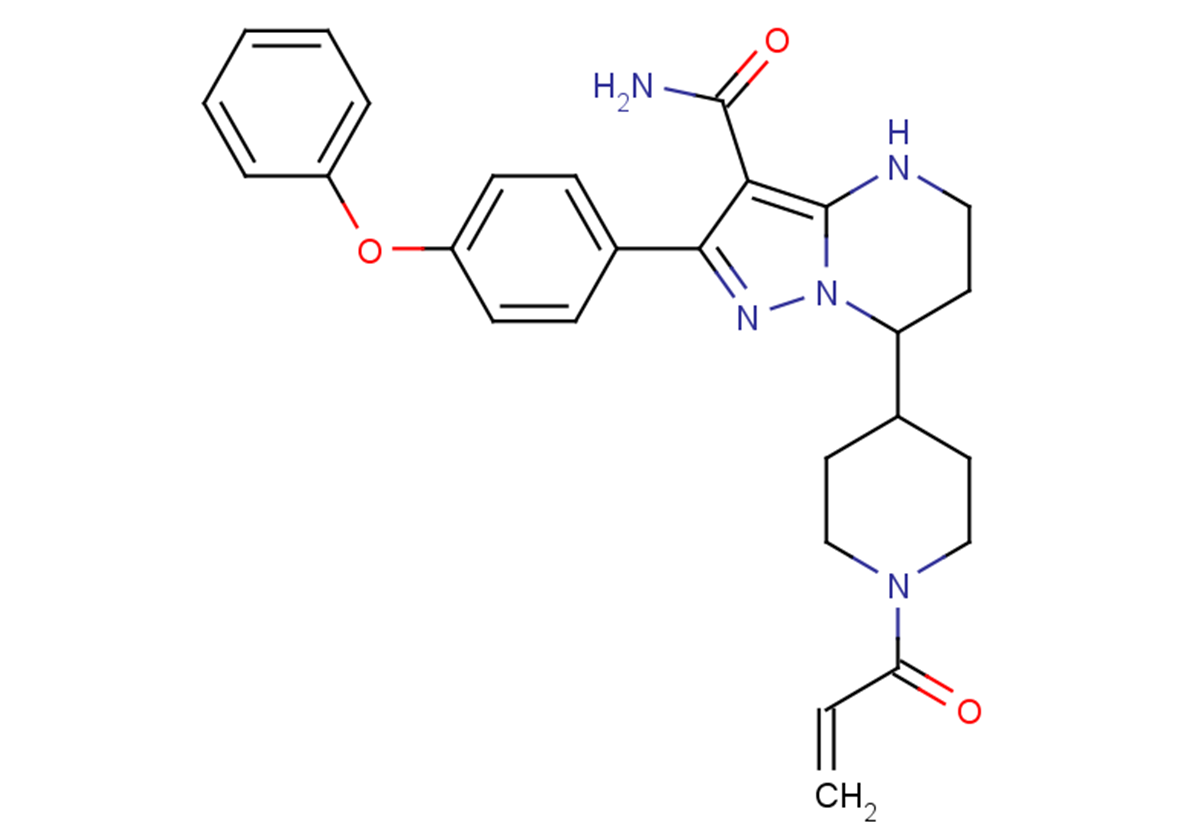
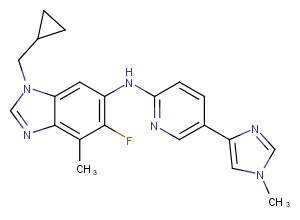
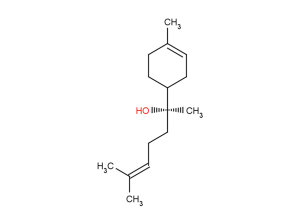
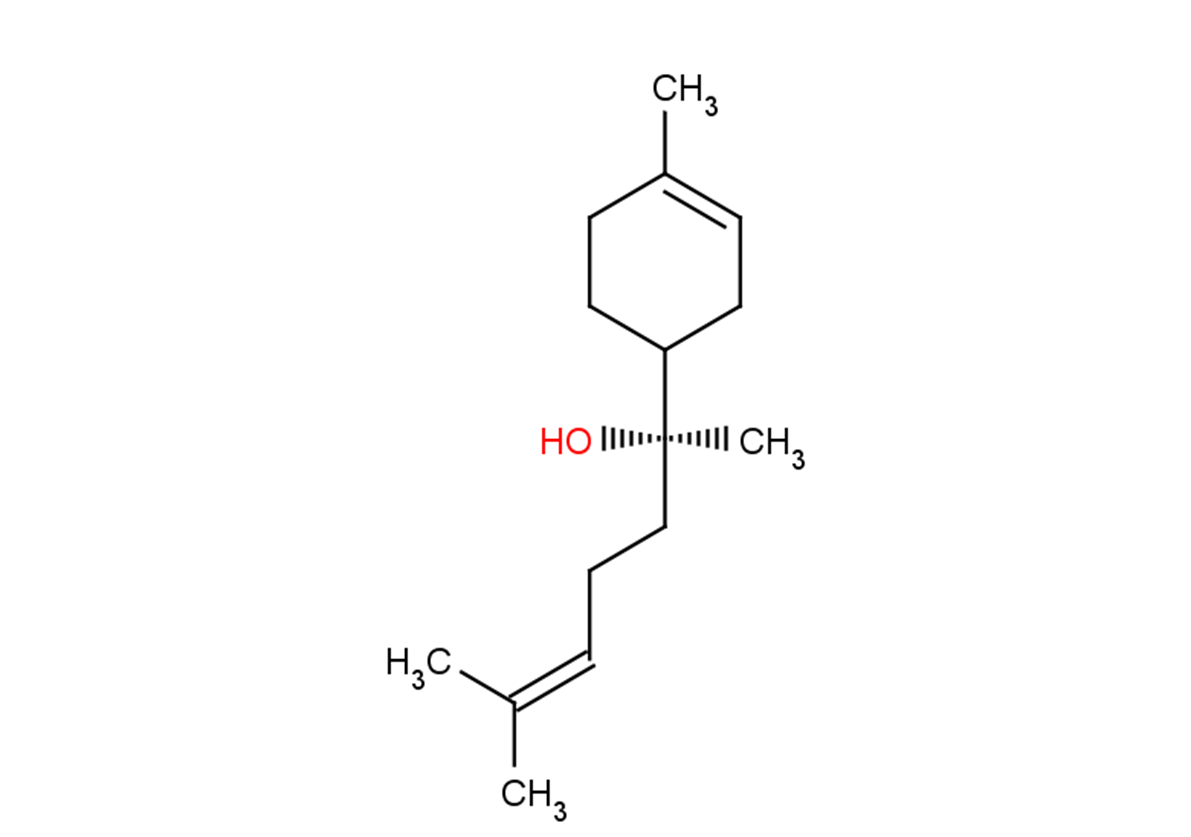
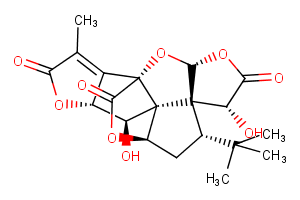
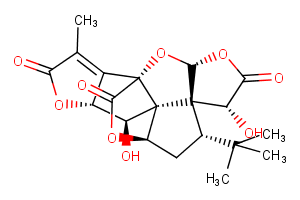
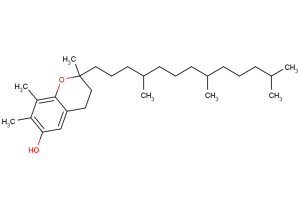
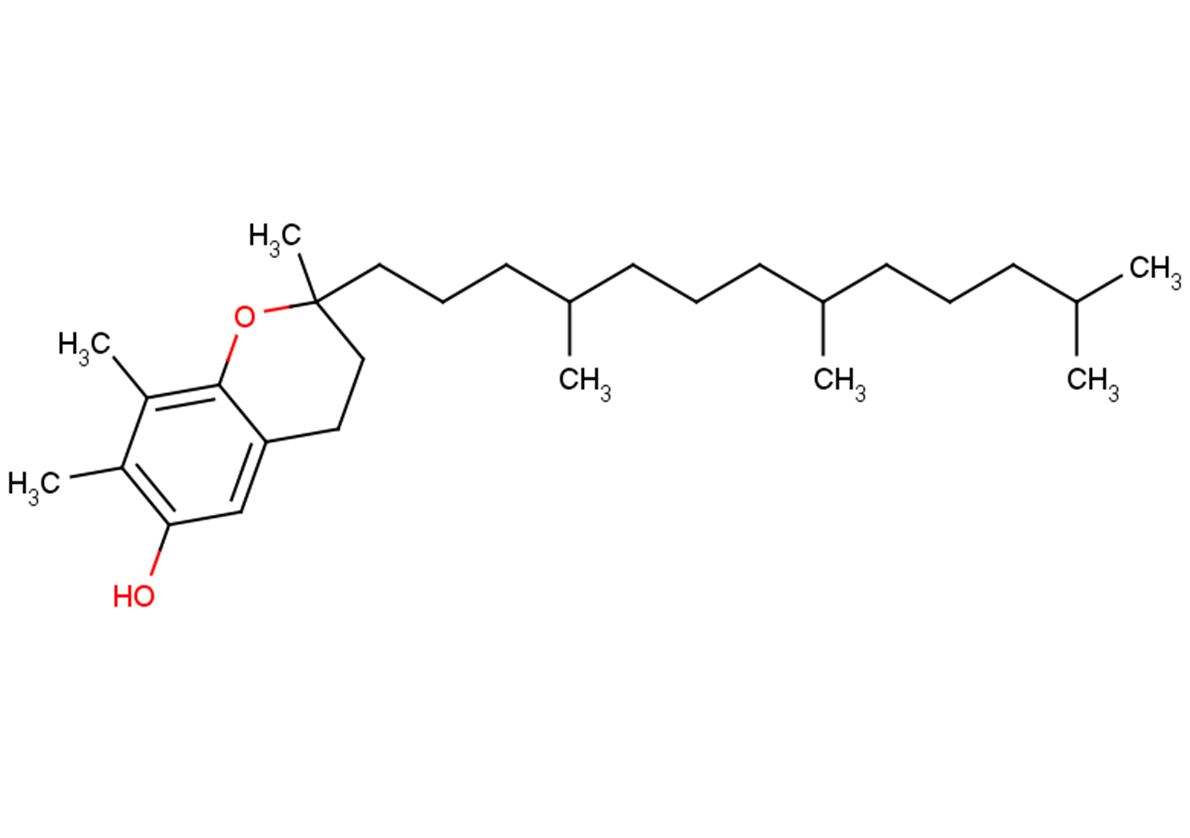
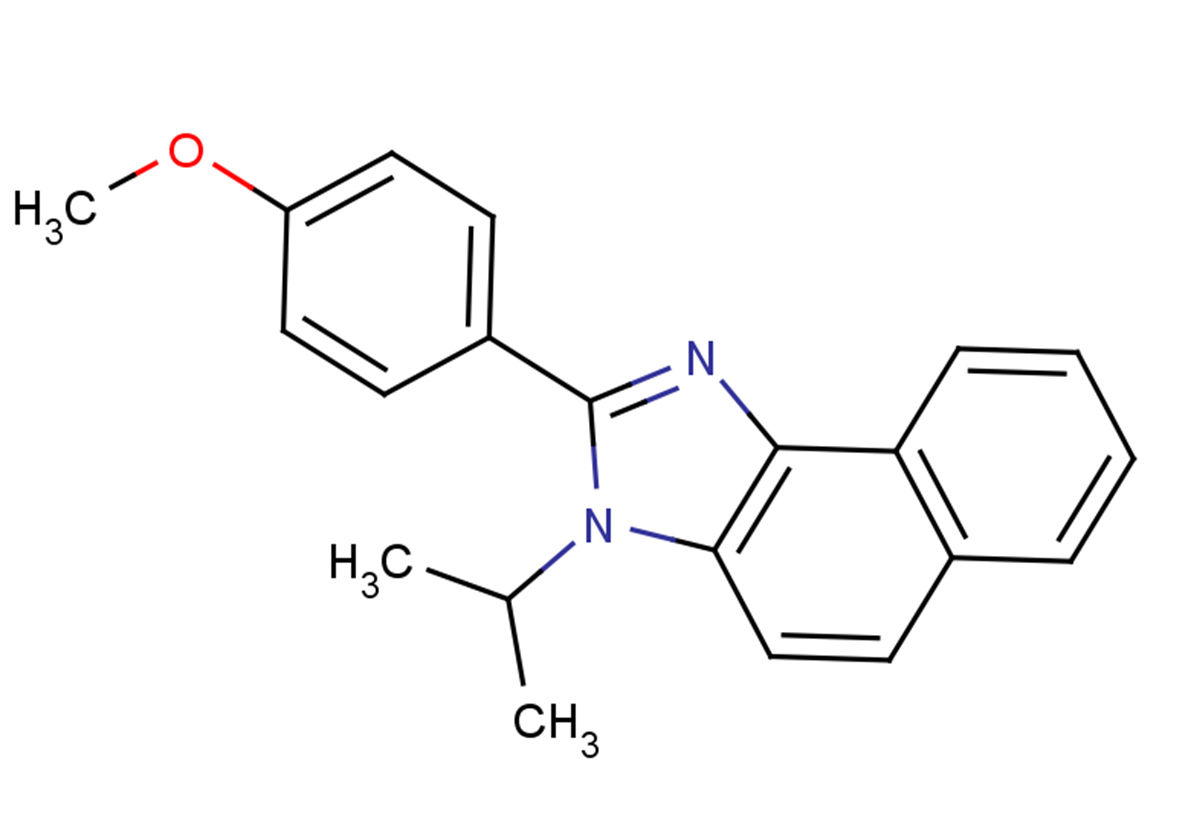
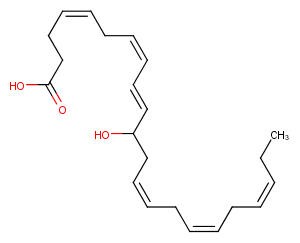
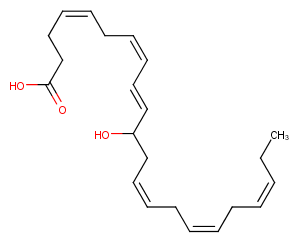
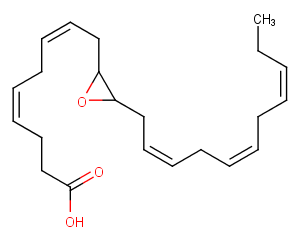
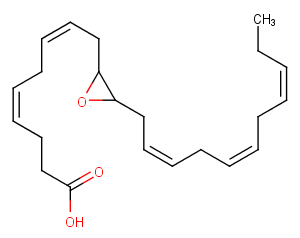
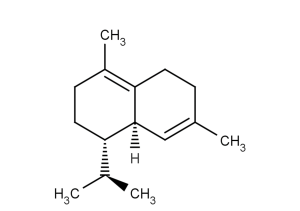
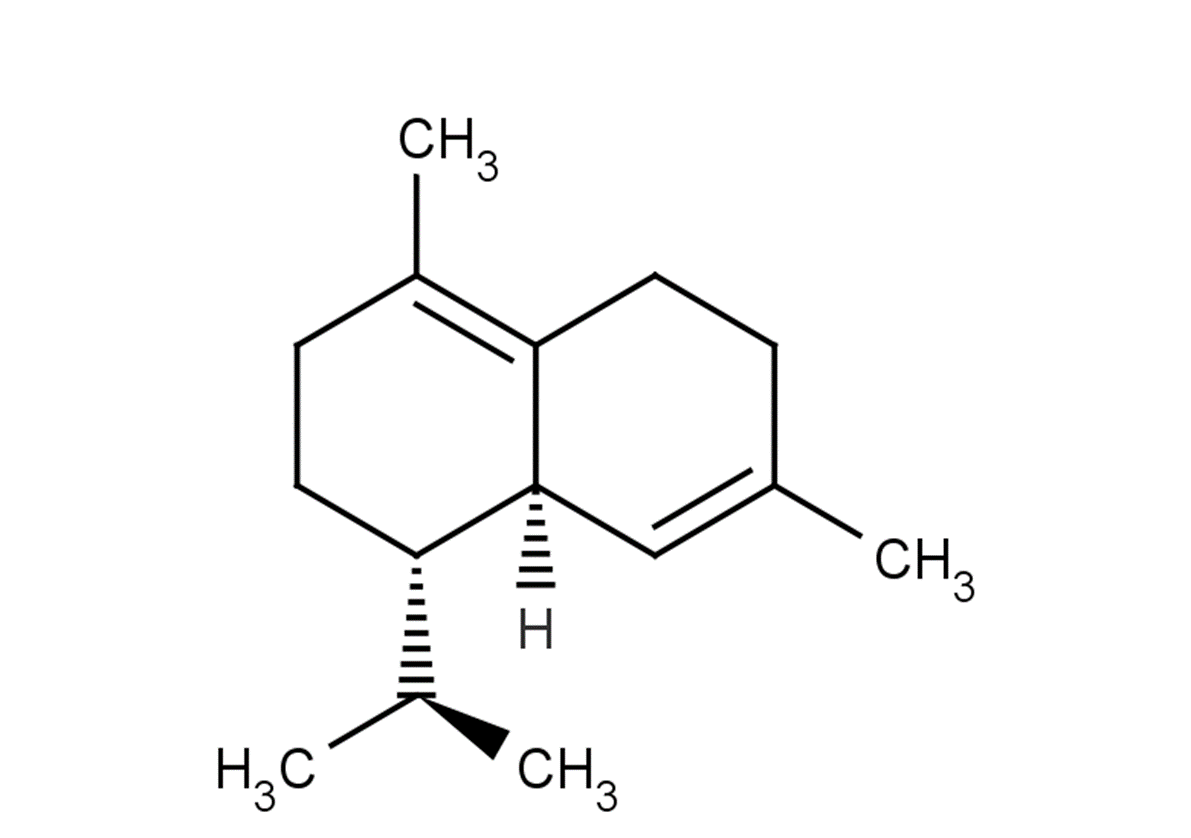
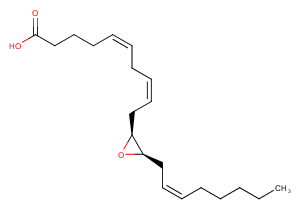
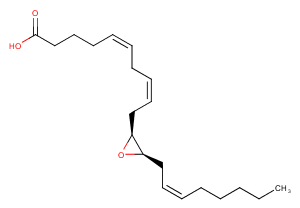
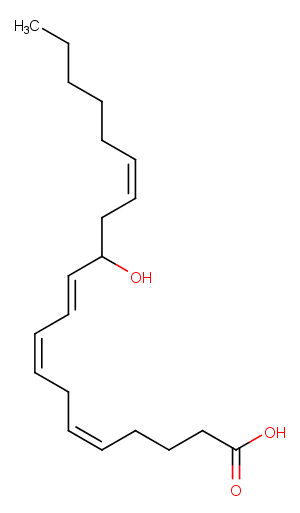
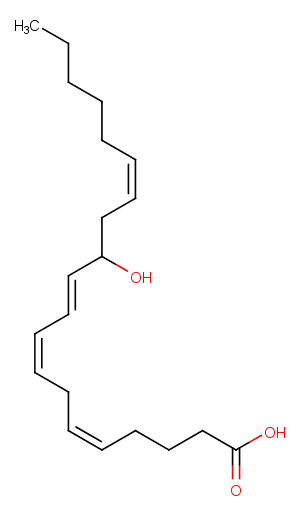
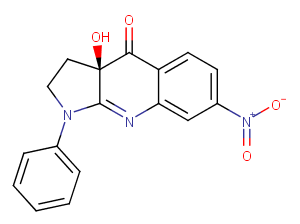
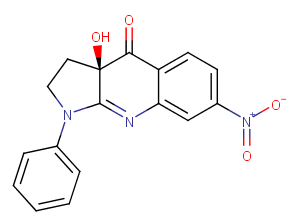
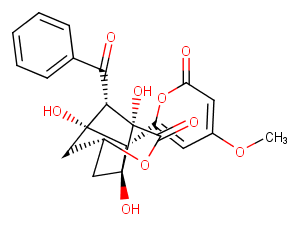
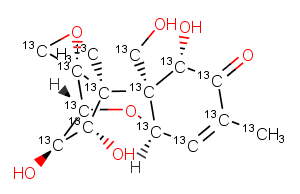
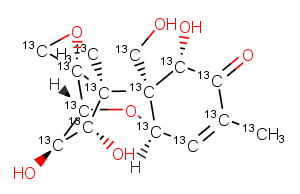
(±)-WS75624B
100 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-Zanubrutinib is a potent and orally available Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor that demonstrates superior oral bioavailability, achieving higher exposure and more complete target inhibi.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-α-Bisabolol isa sesquiterpenol extracted from essential oils of chamomile, candida and other plants. It isa natural antiseptic with soothing, antiirritating, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anticancer activities. (±)-α-Bisabolol has anticancer effects on A549 NSCLC cells by inducing cell cycle arrest, mitochondrial death and inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling (IC50 = 15 μM). (±)-α-Bisabolol can induce apoptosis of glioma cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-α-Bisabolol isa sesquiterpenol extracted from essential oils of chamomile, candida and other plants. It isa natural antiseptic with soothing, antiirritating, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anticancer activities. (±)-α-Bisabolol has anticancer effects on A549 NSCLC cells by inducing cell cycle arrest, mitochondrial death and inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling (IC50 = 15 μM). (±)-α-Bisabolol can induce apoptosis of glioma cells.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays. It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells. (±)-γ-Tocopherol inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays. It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells. (±)-γ-Tocopherol inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays. It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells. (±)-γ-Tocopherol inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible […]
More Information
Supplier Page
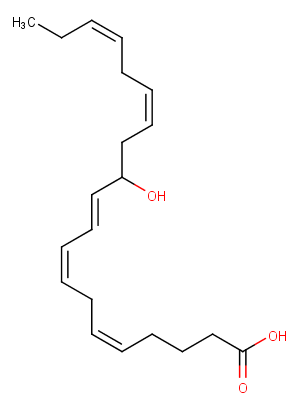
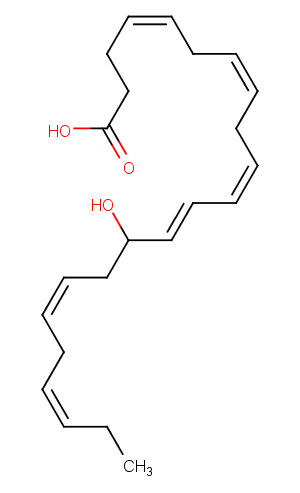
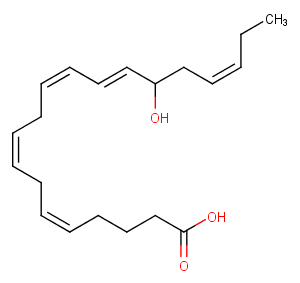
(±)10-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)10-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.[1][2] It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.[3][4][5] (±)10-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
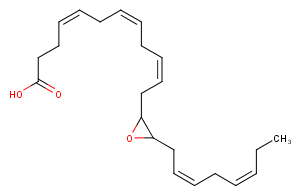
(±)10(11)-DiHDPA is produced from cytochrome P450 epoxygenase action on docosahexaenoic acid . It has been shown to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in mice and may have additional anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 0.43 and 22.5 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively). It is produced though direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases. 10,11-EDP epoxide (12.5 and 25 μM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells. It induces apoptosis […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
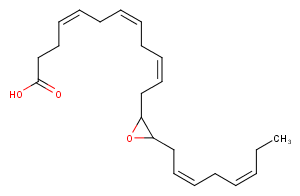
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)10(11)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 10,11-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord, as well as human serum, and acts as a substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km […]
More Information
Supplier Page
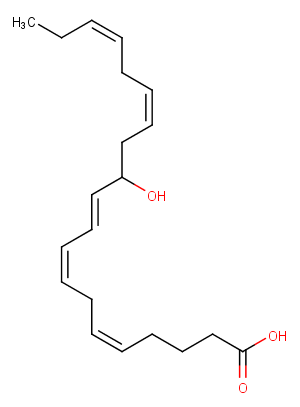
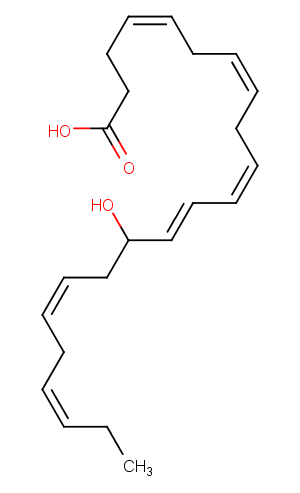
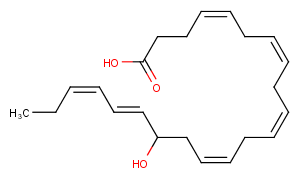
(±)11-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)11-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. DHA is metabolized to 11(S)-HDHA by human platelets and canine retina. In addition to 11(S)-HDHA, 14(S)-HDHA is also produced by platelets. 11(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of […]
More Information
Supplier Page
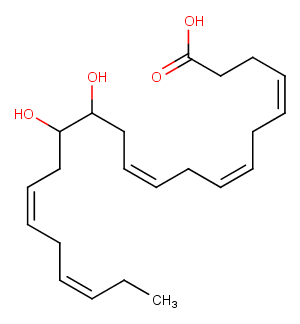
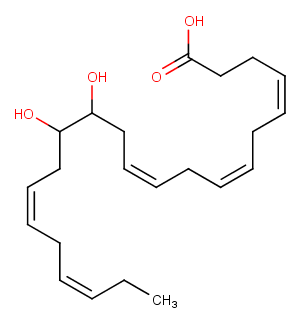
(±)11-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)11-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid . The individual R and S isomers of racemic HETEs have been separated and identified using chiral phase HPLC. The racemic HETEs have been quantified as an index of lipid peroxidation using GC/MS.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
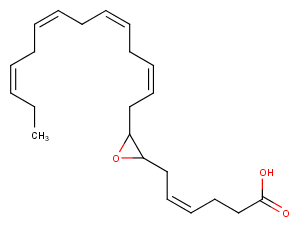
(±)11,12-DiHETE is a dihydroxy metabolite of EPA produced by cytochrome P450-mediated epoxide formation and subsequent hydrolysis by epoxide hydrolase. Plasma levels of (±)11,12-DiHETE are increased over baseline after an oral dose of 1008 mg EPA.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)-11(12)-DiHET is an oxylipin. 11(S),12(S)-DiHET and 11(R),12(R)-DiHET are vicinal diols formedviaenzymatic hydration of 11(12)-EET by cytosolic or soluble epoxide hydrolases in a non-stereoselective manner.1,2,3(±)11(12)-DiHET MaxSpec standard is a quantitative grade standard of (±)11(12)-DiHET that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)11(12)-EET
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)11(12)-EET is a fully racemic version of the R/S enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid by cytochrome P450 enzymes.[1][2][3[]A higher proportion of 11(R),12(S)-EET is produced by the CYP450 isoforms CYP2C23 and CYP2C24 while CYP2B2 produces a higher proportion of 11(S),12(R)-EET.[3]11(12)-EET has been shown, along with 8(9)-EET to play a role in the recovery of depleted […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)12-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)12-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 12(S)-HEPE and 12(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)12-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 12(S) isomer in mammalian systems. 12-HEPE inhibits platelet aggregation with the same potency as 12-HETE, exhibiting IC50 values of 24 and 25 […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME , a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid also known as isoleukotoxin. [1] It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils. [2] 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)13-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)13-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. Fresh water hydra was shown to metabolize DHA to 13(R)-HDHA, presumably via the 11R-lipoxygenase activity. (±)13-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)13-HODE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)13-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. It is the principle hydroxylated fatty acid in human psoriatic skin scales, with a mean concentration of 17 ng/mg.[1]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL. Later studies determined that 15-LO from rabbit reticulocytes and human monocytes were able to metabolize cholesteryl linoleate, a major component of LDL, to 13-HODE cholesteryl ester.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)13(14)-DiHDPA is a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid that is produced via oxidation by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases. Epoxygenase metabolites of DHA, including (±)13(14)-DiHDPA, are reported to inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)13(14)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 13,14-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord and is a preferred substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km value of 3.2 μM. (±)13(14)-EpDPA […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)14-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)14-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. DHA is metabolized to 14(S)-HDHA by human platelets along with 11(S)-HDHA. 14(S)-HDoHE is also produced by salmon gills upon stimulation with calcium ionophore. 14(S)-HDHA was shown to be an […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)14(15)-EET
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)14(15)-EET is a metabolite of arachidonic acid that is formed via epoxidation of arachidonic acid by cytochrome P450.[1],[2] It prevents increases in leukotriene B4, ICAM-1, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 (CCL2) induced by oxidized LDL in primary rat pulmonary artery endothelial cells (RPAECs) when used at a concentration of 1 μM.[3] (±)14(15)-EET induces dilation […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
Arachidonic acid is metabolized in the vascular endothelium to epoxytrienoic acids (EETs or EpETrEs) by cytochrome P450 enzymes. The EETs are released in response to acetylcholine, bradykinin, arachidonic acid, or cyclic stretch. (±)14(15)-EET-SI is the methyl sulfonamide analog of 14(15)-EET. This substitution results in a metabolically more stable compound because it is not sensitive to […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid, also known as dihomo-γ-linolenic acid , is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) produced from γ-linolenic acid by the action of fatty acid elongases. It can be metabolized by the cyclooxygenase pathway to produce 1-series prostaglandins (PGs) (e.g., PGE1). (±)14(15)-EpEDE is an EpEDE acid formed from 8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid. This monoepoxide can be generated from […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
EDHF (endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor) is an unidentified mediator released from vascular endothelial cells in response to acetylcholine and bradykinin which is distinct from the NOS- (nitric oxide) and COX-derived (prostacyclin) vasodilators. Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids, produces epoxides such as (±)14(15)-EpETrE which are prime candidates for the actual active mediator. However, the […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)15-HEDE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)15-HEDE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. There are no reports in the literature of biological activity associated with (±)15-HEDE.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)15-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)15-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 15(S)-HEPE and 15(R)-HEPE. Specific biological activity attributed to (±)15-HEPE has not been documented.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)15-HETE
100 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)15-HETE
500 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)16-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)16-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. (±)16-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)16-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Electrolyte and fluid transport in the kidney are regulated in part by arachidonic acid and its metabolites. (±)16-HETE is the racemic version of a minor CYP450 metabolite of arachidonic acid released by the kidney upon angiotensin II stimulation. The biological activity of 16-HETE is stereospecific. 16(R)-HETE dose-dependently stimulates vasodilation of the rabbit kidney, however 16(S)-HETE […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
EDHF (endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor) is an unidentified mediator released from vascular endothelial cells in response to acetylcholine and bradykinin which is distinct from the NOS- (nitric oxide) and COX-derived (prostacyclin) vasodilators.[1],[2]Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces epoxides such as (±)14(15)-EET which are prime candidates for the actual active mediator.[3] However, the CYP450 […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)17-HDHA
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)17-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid in vitro. It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes. 17(S)-HDHA could be produced by enzymatic oxidation of DHA using soybean lipoxygenase (LO) and is the putative product of mammalian 15-LOs. 17(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of U-46619 […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)17-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
Electrolyte and fluid transport in the kidney are regulated in part by arachidonic acid and its metabolites. (±)17-HETE is the racemic version of a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolite of arachidonic acid that has stereospecific effects on sodium transport in the kidney. At a concentration of 2 μM the (S)-enantiomer of 17-HETE inhibits proximal tubule ATPase […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
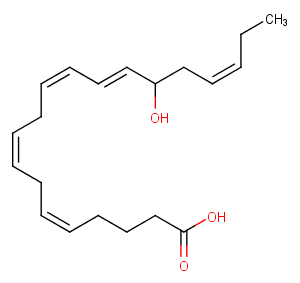
Eicosapentaenoic acid is an ω-3 fatty acid abundantly available in marine organisms. (±)17(18)-DiHETE is one of the major metabolites produced when eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is incubated with various rat tissue homogenates or cynomolgus monkey seminal vesicles. The route of production of (±)17(18)-DiHETE likely proceeds through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation at the ω-3 double bond followed by […]
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)18-HEPE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 18(S)-HEPE and 18(R)-HEPE. Specific biological activity attributed to (±)18-HEPE has not been documented.
More Information
Supplier Page
(±)18-HETE
1 mg
| Purity Not Available
TargetMol
(±)18-HETE is the racemic version of a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolite of arachidonic acid. When formed by the CYP2E1 isoform, 18-HETE is comprised 100% of the (R) isomer. 18(R)-HETE dose-dependently stimulates vasodilation of the rabbit kidney, whereas 18(S)-HETE does not affect perfusion pressure. 18-HETE has negligible effects on ATPase activity. 18(R)-HETE at 1 μM completely […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)19(20)-DiHDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid . It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA via a (±)19(20)-EpDTE intermediate.
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
(±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 108 and 280 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It is produced through direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases. (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide (25 μM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells. It decreases the production of IL-6 […]
More Information
Supplier Page
TargetMol
EDHF (endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor) is an unidentified mediator released from vascular endothelial cells in response to acetylcholine and bradykinin which is distinct from the NOS- (nitric oxide) and COX-derived (prostacyclin) vasodilators. Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces epoxides such as (±)14(15)-EpETrE which are prime candidates for the actual active mediator. However, the […]
More Information
Supplier Page